Part of an ongoing series where I explore the world of NFTs (Part 1, Part 2, Part 3)
Michael Yamashita, a far-east specialist, has been making pictures for National Geographic for over 40 years, and up until 2008, he was the only regularly contributing photographer of color. In addition to over 30 Natgeo magazine assignments over the years, Michael has sold stock, lectured, given workshops, and has made 16 books. In April of last year, Michael started selling his photography as NFTs and is currently listed on Opensea.com as #25 in all-time sales for photography. As someone with such a storied career that has found great success in NFTs, I reached out for an interview.
aPhotoEditor: Let’s start with Instagram. You have 1.8 million followers there. That must help promote any projects you are working on.
Michael Yamashita: It’s great having that many followers from all over the world, but since they changed the algorithm last year, if you are not posting video, you’re not getting any new followers, so Instagram is not as fun anymore for a still photographer. A year ago, I could see 100,000 likes on a post, and now a good post is maybe twenty thousand. And only a small percentage of your followers see all your posts as the formula chooses to send to maybe one-fifth of them. But what we’ve found with Instagram, and this is across the board with my colleagues, is that Instagram people are mostly bucket listers or aspirational travelers. It’s important to be visible on Instagram, but it’s never been a key way to sell anything. We have an occasional book or print sale, but you’d think you’d have more.
When I got involved with NFTs, everyone thought I would pick up sales from my 1.8 million followers, but that didn’t really happen because it’s a very different audience.
aPE: Can you tell me how you got started with NFTs?
MY: Two Harvard MBA grads approached me last year because of my large social media following. And as you know, it’s daunting getting into it; there’s a lot to learn with the vocabulary, dealing with the technical side, and all the Twitter stuff.
The big Beeple sale had just happened, and a bunch of us photographers, all well-known names in the industry, were sitting around trying to figure out how to get into NFTs, and I was the only one who made the leap, and that was mainly because these guys I met were ready to go ahead and help me promote and do what’s necessary to make it happen. We set it up like a photo agency, I chose the photographs, and they handled the technical aspects, and my job was to introduce myself on twitter spaces and get to know the community. It helped that many were already following me on Instagram. Because of that exposure, we got invited into several groups and had several whales who began collecting my work.
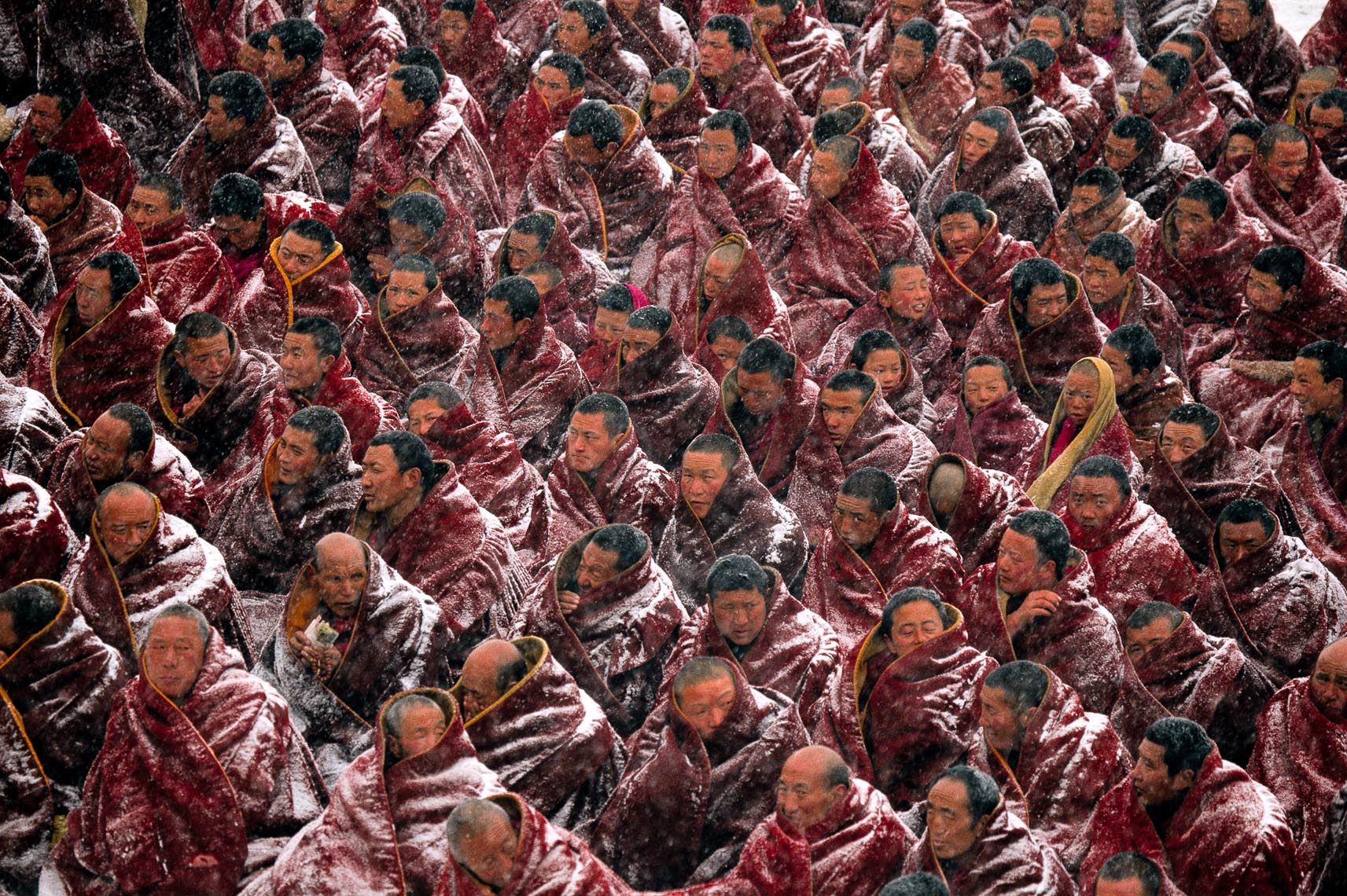
We were told initially that photographs would never sell as Nfts, so we teamed up with an NFT artist who for example took one of my best-known pictures – of Tibetan monks and, using AI, added motion and changing facial expressions to the individual monks and that was my first sale. It was bought by a collector, Drew Marshall, who goes by “hydrate.” He loves photography and happens to live close by, so we became friends. He is now part of my team as a consultant and is involved in our strategy.
aPE: Then didn’t you have a very successful sale on Opensea.com, where you are listed near the top of the sales chart?
MY: The Four Seasons of Jiuzhaigou, my second drop – all straight, non-AI manipulated photographs, took about four months to sell out. It was listed as #24 of the most traded NFT photography collections on OpenSea. And then my 3rd drop of photographs from Tibet was on Nifty Gateway in January, and that sold out in 30 seconds.
aPE: How important is marketing the work and selling out vs. the actual photography?
MY: For the NFT crowd, what makes a great photograph is not necessarily what you would choose as a picture editor who is used to seeing a lot of great photography. It’s more like what appeals to an Instagram crowd, people who just love the picture for whatever reason, but it doesn’t necessarily have to be something critical. There is some crossover between Instagram fans and NFT enthusiasts. I often use Instagram as a measure of how an audience is going to react to a particular photograph; when you see one on Instagram getting huge numbers, you can tell it’s something that grabs the attention of a large crowd, who are reacting emotionally to it.
About half the buyers are in this largely for the investment – they want to resell the work on the secondary market. Your value is often determined by the prices on the secondary market. I’ve had the good fortune that some whales have liked and supported my work. But the quality of the photograph still greatly matters – the cream rises to the top. You look at the big players, and they’re good photographers. You may not have heard of them before, but these guys are good. I have personal favorites, Billy Dinh, John Knoph, Dave Krugman, Reuben Wu. There’s some great photography talent out there. They are primarily a younger crowd; I’m easily the oldest guy in the room. But as I’ve gotten to know them, many have become my friends. The community is extremely enthusiastic and supportive.
aPE: You’ve done assignments for National Geographic, lectures, workshops, sold stock, sold prints, sold books and now NFTs. Can you talk about that progression?
MY: The magazine and photojournalism world has changed dramatically. Stock dried up years ago, and what few magazines are left are not at all the same. The covid years were terrible for photography; even with the PPP loans, I don’t know how anyone made it through the year. I had three assignments and no travel. If I didn’t get involved in the NFT sales, which I began as basically an experiment, I don’t know how I would have made ends meet. But at the same time, I got lucky that covid happened and I was not traveling; otherwise, I don’t think I would even have gotten involved. Being home afforded me the time to travel through my archive, finding the photographs to market as NFTs and getting involved with the community. Things are turning around now, and I’m traveling again, but NFTs are a bright spot for photography right now.
aPE: What advice can you give photographers who want to get involved with NFTs?
MY: I’m fielding many calls from my colleagues, and everybody wants in, but It’s a volatile market so you’ve got to embrace the entire experience and be in it for the long haul. The business is constantly morphing. Starting from ground zero is even more difficult now as many more photographers enter the space. Anyone can do NFT 101, but you’ve got to do the work to get your name out there in front of the community. And that is the issue, the marketing, without any recognition, nobody’s going to look at your stuff. Most big names in photography are not necessarily well known in the NFT space. The market is a community, and they expect NFT creators to be accessible and approachable. You’ve really got to network to get your stuff out there in front of this new group. The events where you can go and meet people are important; the Twitter talks, engaging followers on Twitter and discord, all of which can be a lot of fun. Getting your work on a platform like Super Rare is a big deal because some of the whales only go on a platform which is curated and the highest quality.
There’s been discussion about holding back your best work till you become recognized in the space as you can only mint a photograph one time, but I don’t think you can do that. You’ve got to put your best stuff forward which you can afford to do since remember, you’re not giving up your copyright. Once you become a commodity, you become a safe bet; buyers know your work will go for a certain price, and they know further down the line, they can resell it and make money back on their initial investment.
aPE: And are you ok with a market that is not image driven?
MY: The quality of the work is still the most important for me, and I make sure that my NFTs reflect my best work. Most everyone wants to make money in the space; that’s the name of the game if you’re in there as a photographer. We’ve always been in the business of making pictures and selling them. And if you get down to the basics with professionals, you need to make money in order to do what you love to do. NFTs are just another medium to continue that process; this is their moment. Some young photographers who did not have a showcase to sell their work, went into NFTs and found acceptance there and built these groups around them in which they encouraged each other. And when nobody else was buying, they were buying each other’s stuff. The amazing thing is how open and friendly these groups are to newcomers. A lot of the major money has been made by a small number of people and many have become friends.
aPE: What do you see in the future for NFTs?
MY: It’s not going away. When you’re in the twitter spaces, you meet people from all over the world who are getting into this stuff. I went to the Venice Biennale, and they devoted a whole pavilion to NFTs. Sotheby’s and Christies are involved, and galleries displaying NFTs are popping up in cities and art fairs around the world. The potential is huge, assuming the market is going to come roaring back, which everybody predicts. And it’s a big deal that photographers get 10% in perpetuity every time your work sells. That’s another major motivation for photographers to get into it. There’s not a photographer out there that’s not paying attention to NFTs.
As for the future, it’s likely that the bar will be raised collectively within digital art. Meaning, early adopters may have gotten notoriety and sales simply for showing up and making an effort. With many traditional artists and photographers using NFTs as a medium to sell their work, the overall quality of the work in the top sales category should improve.










 Jonathan Horton of the US Olympic Gymnastics team (Joe Klamar/AFP/Getty Images)
Jonathan Horton of the US Olympic Gymnastics team (Joe Klamar/AFP/Getty Images)
